As we age, the likelihood of developing certain health conditions increases. One of these conditions is osteoarthritis, a type of joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of osteoarthritis and can cause significant pain and mobility issues. In this article, we will explore what knee OA is, its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
What is Knee OA?
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that affects the knee joint. It is a type of arthritis that occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. Without this cartilage, the bones rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Causes of Knee OA
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of knee OA. These include:
- Age: As we age, the risk of developing knee OA increases.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop knee OA.
- Genetics: If you have a family history of knee OA, you may be more likely to develop it.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra stress on the knee joints, which can increase the risk of developing knee OA.
- Injury: A previous knee injury or surgery can increase the risk of developing knee OA.
Symptoms of Knee OA
The symptoms of knee OA can vary from person to person, but the most common ones include:
- Pain: Pain in the knee joint is the most common symptom of knee OA. It may be worse when you move your knee or put weight on it.
- Stiffness: You may feel stiffness in your knee, especially when you first wake up or after sitting for a long time.
- Swelling: Your knee may be swollen or feel warm to the touch.
- Limited mobility: You may have difficulty moving your knee or walking normally.
Diagnosis of Knee OA
If you are experiencing symptoms of knee OA, your doctor may recommend several tests to diagnose the condition. These may include:
- Physical exam: Your doctor will examine your knee and ask you about your symptoms.
- X-rays: X-rays can show the extent of damage to the knee joint.
- MRI: An MRI can provide a detailed image of the knee joint, showing the extent of damage to the cartilage
Treatment of Knee OA
There is no cure for knee OA, but there are several treatments that can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. These include:
Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief of knee OA symptoms.
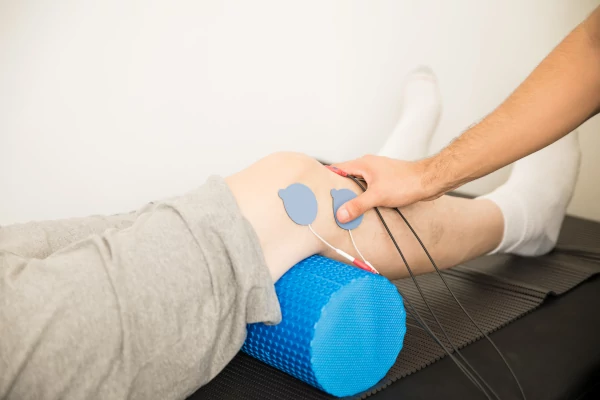
physiotherapy: Physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option for knee osteoarthritis. A physiotherapist can work with you to develop a customized exercise program that can help improve your mobility and reduce pain. The exercises may include low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming, as well as stretching and strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee joint. The physiotherapist may also use manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization to help reduce pain and stiffness. In addition, they can provide guidance on using assistive devices such as braces or crutches to reduce pressure on the knee joint. Overall, physiotherapy can be an important part of a comprehensive treatment plan for knee osteoarthritis.
Weight loss: Losing weight can reduce the stress on the knee joint and slow the progression of knee OA.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to replace the knee joint with an artificial joint.
Prevention of Knee OA
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing knee OA, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight puts extra stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of knee OA.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help keep the muscles around the knee joint strong and reduce the risk of knee OA.
- Avoiding injury: Taking steps to prevent knee injuries, such as wearing protective gear during sports activities, can reduce the risk of knee OA.
Living with Knee OA
Living with knee OA can be challenging, but there are several things you can do to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. These include:
- Using assistive devices: Using a cane or walker can help take pressure off the knee joint and reduce pain.
- Applying heat or cold: Applying heat or cold to the knee joint can help reduce pain and stiffness.
- Practicing good posture: Maintaining good posture can help reduce stress on the knee joint and improve mobility.
- Getting enough rest: Getting enough rest can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint.
Conclusion
Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that can cause significant pain and mobility issues. While there is no cure for knee OA, there are several treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. By maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and taking steps to prevent injury, you can reduce your risk of developing knee OA and improve your quality of life.
FAQs
Can knee OA be cured?
There is no cure for knee OA, but there are several treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Is knee OA a hereditary condition?
While genetics can play a role in the development of knee OA, other factors such as age, gender, obesity, and injury can also contribute to the condition.
Can exercise help reduce symptoms of knee OA?
Yes, low-impact exercise can help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and reduce pain and stiffness.
What types of pain medication are used to treat knee OA?
Over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Is surgery necessary for all cases of knee OA?
Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases of knee OA that do not respond to other treatments.
Check out our article “The Best Exercises for Managing Knee Osteoarthritis.”